redis事件
redis事件
数据结构
//事件处理器状态(同时是时间处理器和文件处理器)
typedef struct aeEventLoop {
//当前注册的最大描述符
int maxfd; /* highest file descriptor currently registered */
//当前追踪的最大描述符
int setsize; /* max number of file descriptors tracked */
//时间事件的id,时间事件链表中记录了最大的id
long long timeEventNextId;
//已注册的文件事件
aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events */
//已经就绪,执行过处理器的文件事件
aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events */
//时间事件
aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead;
//事件处理器开关
int stop;
//多路复用库的私有数据
void *apidata; /* This is used for polling API specific data */
//处理事件之前要执行的函数
aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep;
//处理事件之后要执行的函数
aeBeforeSleepProc *aftersleep;
int flags;
} aeEventLoop;文件事件
服务器通过套接字和客户端连接,文件事件是对于套接字操作的抽象,通信过程会产生相应文件事件,服务器监听处理这些事件
- 本身单线程运行,但是I/O多路复用监听多个套接字
数据结构
/* File event structure
*
* 文件事件结构
*/
typedef struct aeFileEvent {
// 监听事件类型掩码,
// 值可以是 AE_READABLE 或 AE_WRITABLE ,
// 或者 AE_READABLE | AE_WRITABLE
int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) */
// 读事件处理器
aeFileProc *rfileProc;
// 写事件处理器
aeFileProc *wfileProc;
// 多路复用库的私有数据
void *clientData;
} aeFileEvent;构成
套接字
- 每当一个套接字准备好执行某项操作时,产生一个文件事件,一个服务器连接了多个套接字,可以产生多个文件事件
- 当套接字可读(客户端执行write或者close之后)或者有新的可应答套接字出现(新的connect建立)时,产生AE_READABLE事件;套接字变得可写(客户端执行read操作之后)时,产生AE_WRITABLE事件
I/O多路复用程序
- 负责监听多个套接字的上述两种事件,向文件事件分派器传送产生了事件的套接字
- 多个事件时先处理AE_READABLE事件,先读后写,多个套接字都有事件时按照一个队列传送,当上一个套接字的事件处理完毕之后再处理下一个套接字
文件事件分派器
- 根据传来的套接字调用相应的事件处理器
事件处理器
- 执行相关操作的函数
相关API
函数aeCreateFileEvent
/* * 根据 mask 参数的值,监听 fd 文件的状态, * 当 fd 可用时,执行 proc 函数 * 将给定套接字的给定事件加入到I/O多路复用程序的监听范围 * 将事件和事件处理器关联 */ int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask, aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData) { if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) { errno = ERANGE; return AE_ERR; } // 取出文件事件结构 aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1) return AE_ERR; // 设置文件事件类型,以及事件的处理器 fe->mask |= mask; if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc; if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc; // 私有数据 fe->clientData = clientData; // 如果有需要,更新事件处理器的最大 fd if (fd > eventLoop->maxfd) eventLoop->maxfd = fd; return AE_OK; }函数aeDeleteFileEvent
/* * 将 fd 从 mask 指定的监听队列中删除 * i/o多路复用程序取消对给定套接字的给定事件的监听 * 取消事件和事件处理器之间的关联 */ void aeDeleteFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask) { if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) return; // 取出文件事件结构 aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; // 未设置监听的事件类型,直接返回 if (fe->mask == AE_NONE) return; /* We want to always remove AE_BARRIER if set when AE_WRITABLE * is removed. */ if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) mask |= AE_BARRIER; // 取消对给定 fd 的给定事件的监视 aeApiDelEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask); // 计算新掩码 fe->mask = fe->mask & (~mask); if (fd == eventLoop->maxfd && fe->mask == AE_NONE) { /* Update the max fd */ int j; for (j = eventLoop->maxfd-1; j >= 0; j--) if (eventLoop->events[j].mask != AE_NONE) break; eventLoop->maxfd = j; } }函数aeGetFileEvents
/* * 获取给定 fd 正在监听的事件类型 * 返回正在监视的事件类型 */ int aeGetFileEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd) { if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) return 0; aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; return fe->mask; }函数aeWait
/* Wait for milliseconds until the given file descriptor becomes * writable/readable/exception * 在给定毫秒内等待,直到 fd 变成可写、可读或异常 * 事件成功产生或者超时就返回 */ int aeWait(int fd, int mask, long long milliseconds) { struct pollfd pfd; int retmask = 0, retval; memset(&pfd, 0, sizeof(pfd)); pfd.fd = fd; if (mask & AE_READABLE) pfd.events |= POLLIN; if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) pfd.events |= POLLOUT; if ((retval = poll(&pfd, 1, milliseconds))== 1) { if (pfd.revents & POLLIN) retmask |= AE_READABLE; if (pfd.revents & POLLOUT) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE; if (pfd.revents & POLLERR) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE; if (pfd.revents & POLLHUP) retmask |= AE_WRITABLE; return retmask; } else { return retval; } }函数aeApiPoll
/*在指定时间内阻塞并等待所有被aeCreateFileEvent函数设置为监听状态的套接字产生文件事件 当有至少一个事件产生或者超时返回*/ static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp) { aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata; int retval, j, numevents = 0; memcpy(&state->_rfds,&state->rfds,sizeof(fd_set)); memcpy(&state->_wfds,&state->wfds,sizeof(fd_set)); //根据select的retval决定之后的操作 retval = select(eventLoop->maxfd+1, &state->_rfds,&state->_wfds,NULL,tvp); if (retval > 0) { for (j = 0; j <= eventLoop->maxfd; j++) { int mask = 0; aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[j]; //监听得到的事件类型 if (fe->mask == AE_NONE) continue; if (fe->mask & AE_READABLE && FD_ISSET(j,&state->_rfds)) mask |= AE_READABLE; if (fe->mask & AE_WRITABLE && FD_ISSET(j,&state->_wfds)) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; eventLoop->fired[numevents].fd = j; eventLoop->fired[numevents].mask = mask; numevents++; } } else if (retval == -1 && errno != EINTR) { panic("aeApiPoll: select, %s", strerror(errno)); } return numevents; }函数aeProcessEvents
/* 调用aeApiPoll等待事件产生,之后遍历所有产生的事件,处理所有已到达的时间事件,以及所有已就绪的文件事件 * 如果不传入特殊 flags 的话,那么函数睡眠直到文件事件就绪, * 或者下个时间事件到达(如果有的话) * 根据flag值确定相应的处理步骤 * 函数的返回值为已处理事件的数量*/ int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags) { int processed = 0, numevents; /* Nothing to do? return ASAP */ if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0; /* Note that we want to call select() even if there are no * file events to process as long as we want to process time * events, in order to sleep until the next time event is ready * to fire. */ if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 || ((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) { int j; struct timeval tv, *tvp; int64_t usUntilTimer = -1; // 距今最近的时间事件还要多久才能达到,使用usUntilTimer保存 if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT)) usUntilTimer = usUntilEarliestTimer(eventLoop); //还没有到达 if (usUntilTimer >= 0) { tv.tv_sec = usUntilTimer / 1000000; tv.tv_usec = usUntilTimer % 1000000; tvp = &tv; } else { //如果时间事件已经到达(到达间隔时间为负数),将已到达时间事件的到达时间间隔设置为0 /* If we have to check for events but need to return * ASAP because of AE_DONT_WAIT we need to set the timeout * to zero */ // 执行到这一步,说明没有时间事件即将到达 // 那么根据 AE_DONT_WAIT 是否设置来决定是否阻塞,以及阻塞的时间长度 if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) { // 设置文件事件不阻塞,将已到达时间事件的到达时间间隔设置为0 tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0; tvp = &tv; } else { /* Otherwise we can block */ // 文件事件可以阻塞直到有事件到达为止,wait时间设置为无穷 tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */ } } if (eventLoop->flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) { tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0; tvp = &tv; } if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL && flags & AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP) eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop); /* Call the multiplexing API, will return only on timeout or when * some event fires. */ // 处理文件事件,阻塞时间由 tvp 决定 numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp); /* After sleep callback. */ if (eventLoop->aftersleep != NULL && flags & AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP) eventLoop->aftersleep(eventLoop); for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { //从已就绪数组中获取事件 int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd; aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask; int fired = 0; /* Number of events fired for current fd. */ int invert = fe->mask & AE_BARRIER; //读取事件 if (!invert && fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) { //确保读/写事件只能执行其中一个 fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); fired++; fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; /* Refresh in case of resize. */ } /* Fire the writable event. */ //写事件 if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) { if (!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc) { fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); fired++; } } /* If we have to invert the call, fire the readable event now * after the writable one. */ if (invert) { fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; /* Refresh in case of resize. */ if ((fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) && (!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)) { fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); fired++; } } processed++; } } /* Check time events */ //执行时间事件 if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop); return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */ }
文件事件处理器
实现不同的网络通信需求,主要是连接应答处理器,命令请求处理器,命令回复处理器
连接应答处理器
函数acceptTcpHandler对连接服务器监听套接字的客户端进行应答
//创建一个TCP连接 void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) { int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL; char cip[NET_IP_STR_LEN]; UNUSED(el); UNUSED(mask); UNUSED(privdata); while(max--) { //accept客户端连接 cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);//TCP连接函数 if (cfd == ANET_ERR) { if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK) serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr); return; } serverLog(LL_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d", cip, cport); // 为客户端创建客户端状态(redisClient) acceptCommonHandler(connCreateAcceptedSocket(cfd),0,cip); } }redis进行初始化时,将处理器与套接字的AE_READABLE事件连接起来,当由客户端使用sys/socket.h/connect函数连接服务器监听套接字时,套接字产生AE_READABLE事件,引发连接应答处理器执行,并执行相应的套接字应答操作
graph LR a((客户端))--连接监听套接字-->b[服务器:服务器监听套接字产生的AE_READABLE事件,执行连接应答处理器]
命令请求处理器
函数readQueryFromClient从套接字中读入客户端发送的命令请求内容
/* * 读取客户端的查询缓冲区内容 */ void readQueryFromClient(connection *conn) { client *c = connGetPrivateData(conn); int nread, big_arg = 0; size_t qblen, readlen; /* Check if we want to read from the client later when exiting from * the event loop. This is the case if threaded I/O is enabled. */ if (postponeClientRead(c)) return; /* Update total number of reads on server */ //更新server的读入处理计数器 atomicIncr(server.stat_total_reads_processed, 1); readlen = PROTO_IOBUF_LEN; /* If this is a multi bulk request, and we are processing a bulk reply * that is large enough, try to maximize the probability that the query * buffer contains exactly the SDS string representing the object, even * at the risk of requiring more read(2) calls. This way the function * processMultiBulkBuffer() can avoid copying buffers to create the * Redis Object representing the argument. */ if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK && c->multibulklen && c->bulklen != -1 && c->bulklen >= PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG) { ssize_t remaining = (size_t)(c->bulklen+2)-sdslen(c->querybuf); big_arg = 1; /* Note that the 'remaining' variable may be zero in some edge case, * for example once we resume a blocked client after CLIENT PAUSE. */ if (remaining > 0) readlen = remaining; } // 获取查询缓冲区当前内容的长度 // 如果读取出现 short read ,那么可能会有内容滞留在读取缓冲区里面 // 这些滞留内容也许不能完整构成一个符合协议的命令 qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf); //为查询缓冲区分配空间 if (big_arg || sdsalloc(c->querybuf) < PROTO_IOBUF_LEN) { /* When reading a BIG_ARG we won't be reading more than that one arg * into the query buffer, so we don't need to pre-allocate more than we * need, so using the non-greedy growing. For an initial allocation of * the query buffer, we also don't wanna use the greedy growth, in order * to avoid collision with the RESIZE_THRESHOLD mechanism. */ //太长的指令参数只读入一个参数,查询缓冲区不需要多余分配空间,不使用贪心分配空间 c->querybuf = sdsMakeRoomForNonGreedy(c->querybuf, readlen); } else { c->querybuf = sdsMakeRoomFor(c->querybuf, readlen); /* Read as much as possible from the socket to save read(2) system calls. */ readlen = sdsavail(c->querybuf); } //读入内容到查询缓存 nread = connRead(c->conn, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen); //读入出错时 if (nread == -1) { if (connGetState(conn) == CONN_STATE_CONNECTED) { return; } else { serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Reading from client: %s",connGetLastError(c->conn)); freeClientAsync(c); return; } //遇到EOF } else if (nread == 0) { if (server.verbosity <= LL_VERBOSE) { sds info = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(), c); serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Client closed connection %s", info); sdsfree(info); } freeClientAsync(c); return; } else if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) { /* Append the query buffer to the pending (not applied) buffer * of the master. We'll use this buffer later in order to have a * copy of the string applied by the last command executed. */ // 根据内容,更新查询缓冲区(SDS) free 和 len 属性 // 并将 '\0' 正确地放到内容的最后 c->pending_querybuf = sdscatlen(c->pending_querybuf, c->querybuf+qblen,nread); } sdsIncrLen(c->querybuf,nread); qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf); // 如果有需要,更新缓冲区内容长度的峰值(peak) if (c->querybuf_peak < qblen) c->querybuf_peak = qblen; // 记录服务器和客户端最后一次互动的时间 c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime; // 如果客户端是 master 的话,更新它的复制偏移量 if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) c->read_reploff += nread; atomicIncr(server.stat_net_input_bytes, nread); // 查询缓冲区长度超出服务器最大缓冲区长度 // 清空缓冲区并释放客户端 if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) && sdslen(c->querybuf) > server.client_max_querybuf_len) { sds ci = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(),c), bytes = sdsempty(); bytes = sdscatrepr(bytes,c->querybuf,64); serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Closing client that reached max query buffer length: %s (qbuf initial bytes: %s)", ci, bytes); sdsfree(ci); sdsfree(bytes); freeClientAsync(c); return; } /* There is more data in the client input buffer, continue parsing it * in case to check if there is a full command to execute. */ // 从查询缓存重读取内容,创建参数,并执行命令 // 函数会执行到缓存中的所有内容都被处理完为止 processInputBuffer(c); }当一个客户端通过连接应答处理器连接到服务器之后,客户端套接字的AE_READABLE事件和命令请求处理器相关联,当客户端向服务器发送命令请求时,产生AE_READABLE事件引发处理器执行,执行相关套接字读入工作
graph LR a((客户端))--发送命令请求-->b[服务器:客户端套接字产生AE_READABLE事件,执行命令请求处理器]
命令回复处理器
函数sendReplyToClient将服务器执行相关命令得到的命令回复通过套接字返回给客户端
/* * 负责传送命令回复的写处理器 */ void sendReplyToClient(connection *conn) { client *c = connGetPrivateData(conn); writeToClient(c,1);//具体实现 }具体实现的函数如下:
int writeToClient(client *c, int handler_installed) { /* Update total number of writes on server */ //更新写回复计数器 atomicIncr(server.stat_total_writes_processed, 1); ssize_t nwritten = 0, totwritten = 0; size_t objlen; clientReplyBlock *o; //一直循环直到回复缓冲区为空 while(clientHasPendingReplies(c)) { if (c->bufpos > 0) { // 写入内容到套接字 // c->sentlen 是用来处理 short write 的 // 当出现 short write ,导致写入未能一次完成时, // c->buf+c->sentlen 就会偏移到正确(未写入)内容的位置上。 nwritten = connWrite(c->conn,c->buf+c->sentlen,c->bufpos-c->sentlen); //出错时跳出循环 if (nwritten <= 0) break; //写入之后更新写入计数器变量 c->sentlen += nwritten; totwritten += nwritten; /* If the buffer was sent, set bufpos to zero to continue with * the remainder of the reply. */ // 如果缓冲区中的内容已经全部写入完毕 // 那么清空客户端的两个计数器变量 if ((int)c->sentlen == c->bufpos) { c->bufpos = 0; c->sentlen = 0; } } else { //取出位于链表最前面的对象 o = listNodeValue(listFirst(c->reply)); objlen = o->used; //空对象不做处理 if (objlen == 0) { c->reply_bytes -= o->size; listDelNode(c->reply,listFirst(c->reply)); continue; } // 写入内容到套接字 // c->sentlen 是用来处理 short write 的 // 当出现 short write ,导致写入未能一次完成时, // c->buf+c->sentlen 就会偏移到正确(未写入)内容的位置上 nwritten = connWrite(c->conn, o->buf + c->sentlen, objlen - c->sentlen); //写入出错时跳出 if (nwritten <= 0) break; //成功写入时更新计数器变量 c->sentlen += nwritten; totwritten += nwritten; /* If we fully sent the object on head go to the next one */ // 如果缓冲区内容全部写入完毕,那么删除已写入完毕的节点 if (c->sentlen == objlen) { c->reply_bytes -= o->size; listDelNode(c->reply,listFirst(c->reply)); c->sentlen = 0; /* If there are no longer objects in the list, we expect * the count of reply bytes to be exactly zero. */ //list之中没有对象,reply的字节数设置为0 if (listLength(c->reply) == 0) serverAssert(c->reply_bytes == 0); } } /* 为了避免一个非常大的回复独占服务器, * 当写入的总数量大于 REDIS_MAX_WRITE_PER_EVENT , * 临时中断写入,将处理时间让给其他客户端, * 剩余的内容等下次写入就绪再继续写入 * 不过,如果服务器的内存占用已经超过了限制, * 那么为了将回复缓冲区中的内容尽快写入给客户端, * 然后释放回复缓冲区的空间来回收内存, * 这时即使写入量超过了 REDIS_MAX_WRITE_PER_EVENT , * 程序也继续进行写入*/ if (totwritten > NET_MAX_WRITES_PER_EVENT && (server.maxmemory == 0 || zmalloc_used_memory() < server.maxmemory) && !(c->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE)) break; } atomicIncr(server.stat_net_output_bytes, totwritten); //写入出错检测 if (nwritten == -1) { if (connGetState(c->conn) != CONN_STATE_CONNECTED) { serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Error writing to client: %s", connGetLastError(c->conn)); freeClientAsync(c); return C_ERR; } } if (totwritten > 0) { /* For clients representing masters we don't count sending data * as an interaction, since we always send REPLCONF ACK commands * that take some time to just fill the socket output buffer. * We just rely on data / pings received for timeout detection. */ if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER)) c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime; } if (!clientHasPendingReplies(c)) { c->sentlen = 0; /* Note that writeToClient() is called in a threaded way, but * adDeleteFileEvent() is not thread safe: however writeToClient() * is always called with handler_installed set to 0 from threads * so we are fine. *///前面应该是aeDeleteFileEvent() //不能直接删除write handler,因为本身调用就是在线程之中了,aeDeleteFileEvent()线程不安全 if (handler_installed) connSetWriteHandler(c->conn, NULL); /* Close connection after entire reply has been sent. */ // 如果指定了写入之后关闭客户端 FLAG ,那么关闭客户端 if (c->flags & CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY) { freeClientAsync(c); return C_ERR; } } return C_OK; }当访问有命令回复需要传送给客户端的时候将客户端套接字的AE_WRITABLE事件和命令回复处理器相关联,当客户端准备好接受服务器传回的命令回复时,产生AE_WRITABLE事件引发处理器执行,执行相关套接字写入工作
graph RL a[服务器:客户端套接字产生AE_WRITABLE事件,执行命令回复处理器]--发送命令回复-->b((客户端))回复发送之后就接触命令回复处理器和客户端套接字AE_WRITABLE事件之间的关联
全过程:
graph LR a[客户端]--客户端向服务器发送连接请求,服务器执行连接应答处理器-->b[服务器] a--客户端向服务器发送命令请求,服务器执行命令请求处理器-->b b--服务器向客户端发送命令回复,服务器执行命令回复处理器-->a
时间事件
(如serverCron函数)在给定时间点执行,时间事件就是对定时操作的抽象
分类
- 定时事件
- 周期性事件
时间事件的结构
//时间事件的结构,种类包括定时事件和周期性事件
typedef struct aeTimeEvent {
//事件的唯一标识符,从小到大表示从旧到新
long long id; /* time event identifier. */
//事件的到达时间
monotime when;
//时间事件处理器,一个函数
//时间事件的种类决定于这个函数的返回值
//AE_NOMORE表示定时事件,到达一次之后被删除并且不会再次到达
//返回其他整数n表示周期性事件,服务器对事件的when属性进行更新,使之n毫秒之后再次到达
aeTimeProc *timeProc;
//事件释放函数
aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc;
//多路复用库的私有数据
void *clientData;
//指向上一个和下一个时间事件结构,形成链表
struct aeTimeEvent *prev;
struct aeTimeEvent *next;
//防止在迭代过程中周期性事件被释放
int refcount; /* refcount to prevent timer events from being
* freed in recursive time event calls. */
} aeTimeEvent;服务器将时间事件都放在一个链表中,每当时间事件处理器执行时遍历链表,对所有已到达的时间事件调用相应的事件处理器.
新事件放在链表头部,所以链表的头部事件id较大,无序是指when的无序
相关API
函数aeCreateTimeEvent将一个新的时间事件加入到服务器,在当前时间的milliseconds毫秒之后到达
//创建事件计数器 long long aeCreateTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long milliseconds, aeTimeProc *proc, void *clientData, aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc) { //更新时间计数器 long long id = eventLoop->timeEventNextId++; //创建时间事件结构 aeTimeEvent *te; te = zmalloc(sizeof(*te)); if (te == NULL) return AE_ERR; //设置id te->id = id; //设置事件 te->when = getMonotonicUs() + milliseconds * 1000; //设置事件处理器 te->timeProc = proc; te->finalizerProc = finalizerProc; //私有数据 te->clientData = clientData; //将事件插入链表 te->prev = NULL; te->next = eventLoop->timeEventHead; te->refcount = 0; if (te->next) te->next->prev = te; eventLoop->timeEventHead = te; return id; }函数aeDeleteTimeEvent删除给定id的时间事件
//删除给定的时间事件 int aeDeleteTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id) { aeTimeEvent *te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; //遍历链表 while(te) { //发现目标事件 if (te->id == id) { //修改id之后,在processTimeEvents的时候删除 te->id = AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID; return AE_OK; } te = te->next; } return AE_ERR; /* NO event with the specified ID found */ }函数usUntilEarliestTimer返回到达时间距离当前时间最近的时间事件到达耗时
//返回距离第一个时间事件触发的毫秒数 //需要遍历链表,定时一般来说时间事件不多,遍历时间很短 static int64_t usUntilEarliestTimer(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { aeTimeEvent *te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; if (te == NULL) return -1; aeTimeEvent *earliest = NULL; while (te) { if (!earliest || te->when < earliest->when) earliest = te; te = te->next; } monotime now = getMonotonicUs(); return (now >= earliest->when) ? 0 : earliest->when - now; }函数processTimeEvents
//处理到达的时间事件 static int processTimeEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { int processed = 0; aeTimeEvent *te; long long maxId; //遍历链表执行已到达的事件 te = eventLoop->timeEventHead;//指向链表头部 maxId = eventLoop->timeEventNextId-1; monotime now = getMonotonicUs(); while(te) { long long id; /* Remove events scheduled for deletion. */ //之前id已经设置为AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID的事件需要删除掉 if (te->id == AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID) { aeTimeEvent *next = te->next; /* If a reference exists for this timer event, * don't free it. This is currently incremented * for recursive timerProc calls */ if (te->refcount) {//有迭代子程序调用的事件不删除 te = next; continue; } //修改相关的指针 if (te->prev) te->prev->next = te->next; else eventLoop->timeEventHead = te->next; if (te->next) te->next->prev = te->prev; //执行清理处理器 if (te->finalizerProc) { te->finalizerProc(eventLoop, te->clientData); now = getMonotonicUs(); } //释放要删除的时间事件 zfree(te); te = next; continue; } /* Make sure we don't process time events created by time events in * this iteration. Note that this check is currently useless: we always * add new timers on the head, however if we change the implementation * detail, this check may be useful again: we keep it here for future * defense. */ //无效事件跳过 if (te->id > maxId) { te = te->next; continue; } //当前时间大于等于时间事件的when,事件已到达,执行这个事件 if (te->when <= now) { int retval; id = te->id; te->refcount++; //执行对应的文件处理器,记录返回值 retval = te->timeProc(eventLoop, id, te->clientData); te->refcount--; processed++; now = getMonotonicUs(); //区分是否是定时事件 if (retval != AE_NOMORE) { //retval毫秒之后再次执行 te->when = now + retval * 1000; } else { //直接删除 te->id = AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID; } } te = te->next; } return processed; }serverCron就是非常典型的周期性时间事件,服务器只要在运行就要周期性运行这个函数
redis运行流程
graph LR
id1[启动服务器]-->id7[配置和加载初始化]-->id8[创建事件循环]-->id10[开始socket监听]
-->id9[向循环事件中注册serverCron]
subgraph 循环
id9-->
id2{是否关闭服务器}--否-->id4[等待文件事件产生]
id4-->id5[处理产生的文件事件]-->id6[处理已到达的时间事件]--开始新的事件循环-->id2
end
id2--是-->id3[关闭服务器]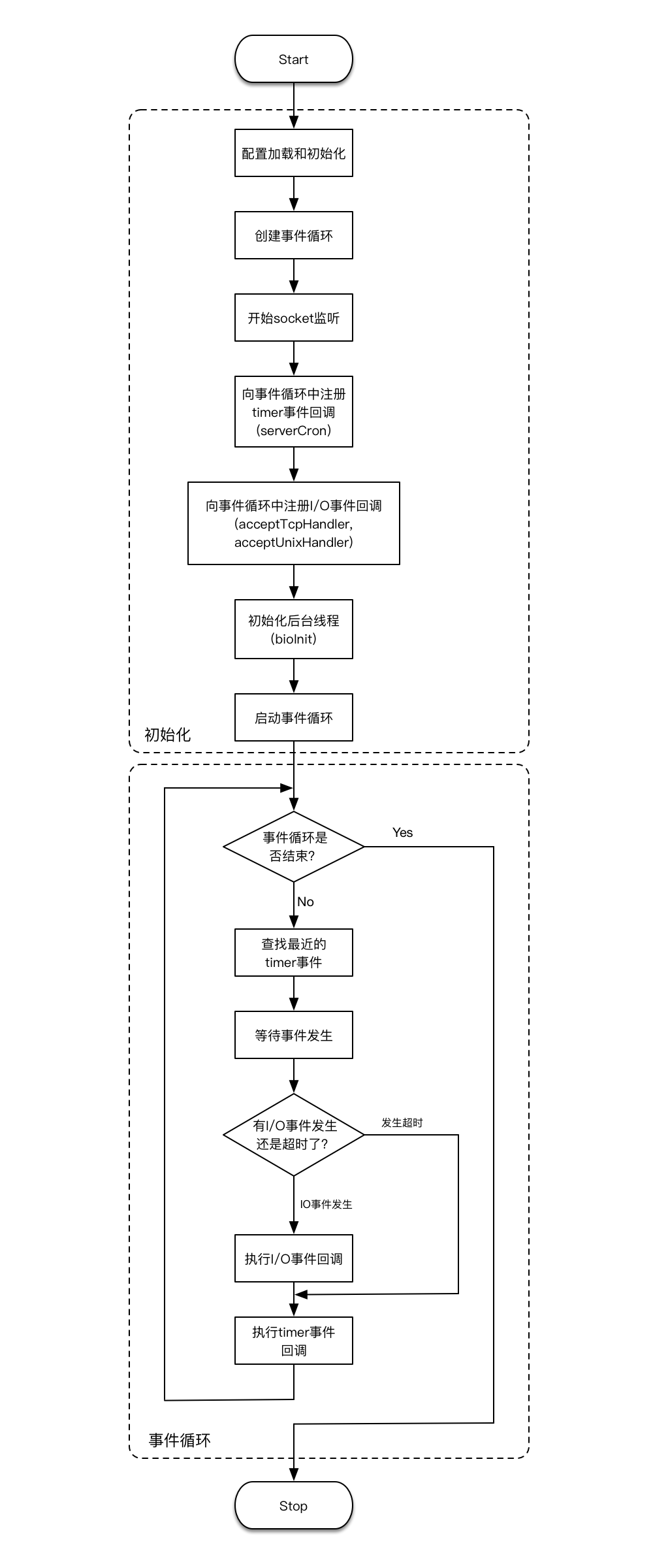
两张图的方式都差不多,展示了整个redis的过程
