redis客户端与服务器
redis客户端与服务器
客户端
cli命令行
typedef struct multiCmd { //参数 robj **argv; //参数数量 int argc; //命令指针 struct redisCommand *cmd; } multiCmd;client结构(直接对于所有的数据结构进行了解释)
//I/O复用,所以需要为每个客户端维持一个状态,多个客户端在服务器用链表链接 typedef struct client { //client的id uint64_t id; /* Client incremental unique ID. */ connection *conn; //协议版本 int resp; /* RESP protocol version. Can be 2 or 3. */ //当前正在使用的数据库 redisDb *db; /* Pointer to currently SELECTed DB. */ //客户端名字 robj *name; /* As set by CLIENT SETNAME. */ //缓冲区,用于储存指令 sds querybuf; /* Buffer we use to accumulate client queries. */ //在指令缓冲区中已经读到的位置 size_t qb_pos; /* The position we have read in querybuf. */ sds pending_querybuf; /* If this client is flagged as master, this buffer represents the yet not applied portion of the replication stream that we are receiving from the master. */ //最近时间内缓冲区长度最大值 size_t querybuf_peak; /* Recent (100ms or more) peak of querybuf size. */ //当前指令的参数数量 int argc; /* Num of arguments of current command. */ //当前指令参数值 robj **argv; /* Arguments of current command. */ //参数有可能是重写过的,记录了原来的参数数量 int original_argc; /* Num of arguments of original command if arguments were rewritten. */ //参数有可能是重写过的,记录了原来的参数值 robj **original_argv; /* Arguments of original command if arguments were rewritten. */ size_t argv_len_sum; /* Sum of lengths of objects in argv list. */ //记录客户端执行的命令 struct redisCommand *cmd, *lastcmd; /* Last command executed. */ //与之前定义的user对应,从而赋予相应的权限,NULL是管理员 user *user; /* User associated with this connection. If the user is set to NULL the connection can do anything (admin). */ //指令类型,一条指令还是多条(内联) int reqtype; /* Request protocol type: PROTO_REQ_* */ //还未读取的指令数量 int multibulklen; /* Number of multi bulk arguments left to read. */ //未读指令的 long bulklen; /* Length of bulk argument in multi bulk request. */ //回复链表 list *reply; /* List of reply objects to send to the client. */ //回复链表中对象的总大小 unsigned long long reply_bytes; /* Tot bytes of objects in reply list. */ // 已发送字节,用于处理 short write size_t sentlen; /* Amount of bytes already sent in the current buffer or object being sent. */ //创建客户端时间 time_t ctime; /* Client creation time. */ long duration; /* Current command duration. Used for measuring latency of blocking/non-blocking cmds */ // 客户端最后一次和服务器互动的时间 time_t lastinteraction; /* Time of the last interaction, used for timeout */ time_t obuf_soft_limit_reached_time; //客户端状态CLIENT_* uint64_t flags; /* Client flags: CLIENT_* macros. */ int authenticated; /* Needed when the default user requires auth. */ //复制状态 int replstate; /* Replication state if this is a slave. */ int repl_put_online_on_ack; /* Install slave write handler on first ACK. */ // 用于保存主服务器传来的 RDB 文件的文件描述符 int repldbfd; /* Replication DB file descriptor. */ // 读取主服务器传来的 RDB 文件的偏移量 off_t repldboff; /* Replication DB file offset. */ // 主服务器传来的 RDB 文件的大小 off_t repldbsize; /* Replication DB file size. */ sds replpreamble; /* Replication DB preamble. */ long long read_reploff; /* Read replication offset if this is a master. */ // 主服务器的复制偏移量 long long reploff; /* Applied replication offset if this is a master. */ // 从服务器最后一次发送 REPLCONF ACK 时的偏移量 long long repl_ack_off; /* Replication ack offset, if this is a slave. */ // 从服务器最后一次发送 REPLCONF ACK 的时间 long long repl_ack_time;/* Replication ack time, if this is a slave. */ long long repl_last_partial_write; /* The last time the server did a partial write from the RDB child pipe to this replica */ long long psync_initial_offset; /* FULLRESYNC reply offset other slaves copying this slave output buffer should use. */ // 主服务器的 master run ID // 保存在客户端,用于执行部分重同步 char replid[CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE+1]; /* Master replication ID (if master). */ // 从服务器的监听端口号 int slave_listening_port; /* As configured with: REPLCONF listening-port */ char *slave_addr; /* Optionally given by REPLCONF ip-address */ int slave_capa; /* Slave capabilities: SLAVE_CAPA_* bitwise OR. */ //事务状态 multiState mstate; /* MULTI/EXEC state */ //阻塞类型 int btype; /* Type of blocking op if CLIENT_BLOCKED. */ //阻塞状态 blockingState bpop; /* blocking state */ // 最后被写入的全局复制偏移量 long long woff; /* Last write global replication offset. */ list *watched_keys; /* Keys WATCHED for MULTI/EXEC CAS */ // 这个字典记录了客户端所有订阅的频道 // 键为频道名字,值为 NULL // 也即是,一个频道的集合 dict *pubsub_channels; /* channels a client is interested in (SUBSCRIBE) */ // 链表,包含多个 pubsubPattern 结构 // 记录了所有订阅频道的客户端的信息 // 新 pubsubPattern 结构总是被添加到表尾 list *pubsub_patterns; /* patterns a client is interested in (SUBSCRIBE) */ sds peerid; /* Cached peer ID. */ sds sockname; /* Cached connection target address. */ listNode *client_list_node; /* list node in client list */ listNode *paused_list_node; /* list node within the pause list */ RedisModuleUserChangedFunc auth_callback; /* Module callback to execute * when the authenticated user * changes. */ void *auth_callback_privdata; /* Private data that is passed when the auth * changed callback is executed. Opaque for * Redis Core. */ void *auth_module; /* The module that owns the callback, which is used * to disconnect the client if the module is * unloaded for cleanup. Opaque for Redis Core.*/ /* If this client is in tracking mode and this field is non zero, * invalidation messages for keys fetched by this client will be send to * the specified client ID. */ uint64_t client_tracking_redirection; rax *client_tracking_prefixes; /* A dictionary of prefixes we are already subscribed to in BCAST mode, in the context of client side caching. */ /* In clientsCronTrackClientsMemUsage() we track the memory usage of * each client and add it to the sum of all the clients of a given type, * however we need to remember what was the old contribution of each * client, and in which category the client was, in order to remove it * before adding it the new value. */ uint64_t client_cron_last_memory_usage; int client_cron_last_memory_type; /* Response buffer */ // 回复偏移量 int bufpos; size_t buf_usable_size; /* Usable size of buffer. */ /* Note that 'buf' must be the last field of client struct, because memory * allocator may give us more memory than our apply for reducing fragments, * but we want to make full use of given memory, i.e. we may access the * memory after 'buf'. To avoid make others fields corrupt, 'buf' must be * the last one. */ //回复缓冲区 char buf[PROTO_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES]; } client;所有的client属性连成了一个链表,保存在redisServer的clients属性中,对于不同状态的client也有其他的链表保存.
struct redisServer { //... //链表,保存了所有的客户端状态 list *clients; /* List of active clients */ //保存所有的待关闭客户端 list *clients_to_close; /* Clients to close asynchronously */ //将要写的客户端列表 list *clients_pending_write; /* There is to write or install handler. */ //将要读的客户端列表(已经知道有指令输入了) list *clients_pending_read; /* Client has pending read socket buffers. */ //... };
客户端属性
包含通用属性(所有客户端执行基础功能都必须需要的)和特定功能(执行特定功能)相关的属性
套接字描述符uint64_t id;
- 伪客户端:id为-1,载入AOF文件时使用,或者是执行Lua脚本中包含的redis命令
- 普通客户端的id大于-1,表示是正常的客户端
名字robj *name;
- 可有可无,一个robj对象,没有的时候指定为NULL
标志uint64_t flags;
表示了当前客户端的角色和状态
可以是单个也可以是多个标志的二进制取或.见CLIENT_*的定义可知,都是一位表示的
源代码:
/* Client flags */ //主从服务器进行复制时,相互都是客户端的关系,slave和master区分两个服务器 #define CLIENT_SLAVE (1<<0) /* This client is a replica */ #define CLIENT_MASTER (1<<1) /* This client is a master */ //正在执行monitor指令,是一个从客户端 #define CLIENT_MONITOR (1<<2) /* This client is a slave monitor, see MONITOR */ //执行事务 #define CLIENT_MULTI (1<<3) /* This client is in a MULTI context */ //客户端被阻塞 #define CLIENT_BLOCKED (1<<4) /* The client is waiting in a blocking operation */ //事务使用WATCH监视的数据库键已经被修改,EXEC执行过程中会直接fail #define CLIENT_DIRTY_CAS (1<<5) //用户对这个客户端执行了 CLIENT KILL命令或者客户端发送给服务器的命令中协议内容有误, //服务器会将客户端积存在输出缓冲区中的所有内容发送给客户端,然后关闭客户端 #define CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY (1<<6) /* Close after writing entire reply. */ //从阻塞中解除,只有在之前阻塞过才可用 #define CLIENT_UNBLOCKED (1<<7) /* This client was unblocked and is stored in server.unblocked_clients */ //专门处理Lua脚本的客户端 #define CLIENT_LUA (1<<8) /* This is a non connected client used by Lua */ //客户端向集群节点( 运行在集群模式下的服务器) 发送了ASKING 命令 #define CLIENT_ASKING (1<<9) /* Client issued the ASKING command */ //客户端的输出缓冲区大小超出了服务器允许的范围, //服务器会在下一次执行 serverCron 函数时关闭这个客户端,以免影响服务器的稳定性 //积存在输出缓冲区中的所有内容会直接被释放,不会返回给客户端. #define CLIENT_CLOSE_ASAP (1<<10)/* Close this client ASAP */ //服务器使用 UNIX 套接字来连接客户端 #define CLIENT_UNIX_SOCKET (1<<11) /* Client connected via Unix domain socket */ //事务在命令入队时出现了错误, 和CLIENT_DIRTY_CAS 都表示了事务不安全,EXEC会执行失败 #define CLIENT_DIRTY_EXEC (1<<12) /* EXEC will fail for errors while queueing */ //在主从服务器进行命令传播期间,从服务器需要向主服务器发送REPLICATION ACK命令 //发送命令之前需要打开这个标志以允许发送操作执行 #define CLIENT_MASTER_FORCE_REPLY (1<<13) /* Queue replies even if is master */ //执行PUBSUB指令时打开,强制服务器将当前执行的命令写人到 AOF 文件里面 #define CLIENT_FORCE_AOF (1<<14) /* Force AOF propagation of current cmd. */ //执行SCRIPT LOADD指令时打开,强制主服务器将当前执行的命令复制给所有从服务器 #define CLIENT_FORCE_REPL (1<<15) /* Force replication of current cmd. */ //主服务器不能使用PSYNC命令与当前低版本从服务器进行同步. //这个标志只能在 REDIS_SLAVE 标志处于打开状态时使用 #define CLIENT_PRE_PSYNC (1<<16) /* Instance don't understand PSYNC. */ #define CLIENT_READONLY (1<<17) /* Cluster client is in read-only state. */ #define CLIENT_PUBSUB (1<<18) /* Client is in Pub/Sub mode. */ #define CLIENT_PREVENT_AOF_PROP (1<<19) /* Don't propagate to AOF. */ #define CLIENT_PREVENT_REPL_PROP (1<<20) /* Don't propagate to slaves. */ #define CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP (CLIENT_PREVENT_AOF_PROP|CLIENT_PREVENT_REPL_PROP) #define CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE (1<<21) /* Client has output to send but a write handler is yet not installed. */ #define CLIENT_REPLY_OFF (1<<22) /* Don't send replies to client. */ #define CLIENT_REPLY_SKIP_NEXT (1<<23) /* Set CLIENT_REPLY_SKIP for next cmd */ #define CLIENT_REPLY_SKIP (1<<24) /* Don't send just this reply. */ #define CLIENT_LUA_DEBUG (1<<25) /* Run EVAL in debug mode. */ #define CLIENT_LUA_DEBUG_SYNC (1<<26) /* EVAL debugging without fork() */ #define CLIENT_MODULE (1<<27) /* Non connected client used by some module. */ #define CLIENT_PROTECTED (1<<28) /* Client should not be freed for now. */ #define CLIENT_PENDING_READ (1<<29) /* The client has pending reads and was put in the list of clients we can read from. */ #define CLIENT_PENDING_COMMAND (1<<30) /* Indicates the client has a fully * parsed command ready for execution. */ #define CLIENT_TRACKING (1ULL<<31) /* Client enabled keys tracking in order to perform client side caching. */ #define CLIENT_TRACKING_BROKEN_REDIR (1ULL<<32) /* Target client is invalid. */ #define CLIENT_TRACKING_BCAST (1ULL<<33) /* Tracking in BCAST mode. */ #define CLIENT_TRACKING_OPTIN (1ULL<<34) /* Tracking in opt-in mode. */ #define CLIENT_TRACKING_OPTOUT (1ULL<<35) /* Tracking in opt-out mode. */ #define CLIENT_TRACKING_CACHING (1ULL<<36) /* CACHING yes/no was given, depending on optin/optout mode. */ #define CLIENT_TRACKING_NOLOOP (1ULL<<37) /* Don't send invalidation messages about writes performed by myself.*/ #define CLIENT_IN_TO_TABLE (1ULL<<38) /* This client is in the timeout table. */ #define CLIENT_PROTOCOL_ERROR (1ULL<<39) /* Protocol error chatting with it. */ #define CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_COMMAND (1ULL<<40) /* Close after executing commands * and writing entire reply. */ #define CLIENT_DENY_BLOCKING (1ULL<<41) /* Indicate that the client should not be blocked. currently, turned on inside MULTI, Lua, RM_Call, and AOF client */ #define CLIENT_REPL_RDBONLY (1ULL<<42) /* This client is a replica that only wants RDB without replication buffer. */PUBSUB命令:本身不修改数据库,但是向频道的所有订阅者发送消息的行为带有副作用, 接收到消息的所有客户端的状态都会因为这个命令而改变,所以也需要写入AOF.
SCRIPT LOAD命令:类似的,它修改了服务器状态,也带有副作用,同时因为涉及到主从服务器,CLIENT_FORCE_REPL将指令发给所有的从服务器.
输入缓冲区
源代码:
typedef struct client { //缓冲区,用于储存指令 sds querybuf; /* Buffer we use to accumulate client queries. */ }client;保存用户发送的命令请求,根据输入内容动态变化大小
命令和命令参数
源代码:
typedef struct client { //当前指令的参数数量 int argc; /* Num of arguments of current command. */ //当前指令参数值 robj **argv; /* Arguments of current command. */ //参数有可能是重写过的,记录了原来的参数数量 int original_argc; /* Num of arguments of original command if arguments were rewritten. */ //参数有可能是重写过的,记录了原来的参数值 robj **original_argv; /* Arguments of original command if arguments were rewritten. */ size_t argv_len_sum; /* Sum of lengths of objects in argv list. */ }client;
命令实现函数
源代码:
typedef struct client { //记录客户端执行的命令 struct redisCommand *cmd, *lastcmd; /* Last command executed. */ }client;根据项argv[0] 的值,在命令表中査找命令所对应的命令实现函数,找到之后将客户端状态的cmd执行那个在命令表之中的这个结构,这个结构保存了命令的实现函数、 命令的标志 、 命令应该给定的参数个数、 命令的总执行次数和总消耗时长等统计信息
输出缓冲区
源代码:
typedef struct client { //... /* Response buffer */ // 回复偏移量 int bufpos; size_t buf_usable_size; /* Usable size of buffer. */ /* Note that 'buf' must be the last field of client struct, because memory * allocator may give us more memory than our apply for reducing fragments, * but we want to make full use of given memory, i.e. we may access the * memory after 'buf'. To avoid make others fields corrupt, 'buf' must be * the last one. */ //回复缓冲区,放在最后,因为内存分配的时候可能多给了一些内存,实际上并没有用到 char buf[PROTO_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES]; } client;当 buf 数组的空间已经用完,或者回复因为太大而没办法放进 buf 数组里面时, 服务器就会开始使用可变大小缓冲区
list *reply;,一个链表连接多个字符串对象,可以保存很长的回复信息
身份验证
- int authenticated;
- 启用了身份验证之后,当属性为0时,除了AUTH指令,其他指令都会被拒绝.
时间
源代码:
//创建客户端时间 time_t ctime; /* Client creation time. */ long duration; /* Current command duration. Used for measuring latency of blocking/non-blocking cmds */ // 客户端最后一次和服务器互动的时间 ,即客户端空转时间 time_t lastinteraction; /* Time of the last interaction, used for timeout */ //达到buf软性限制的时间,太长的话会被kill time_t obuf_soft_limit_reached_time;
限制缓冲区大小
- 硬性限制( hard limit ): 如果输出缓冲区的大小超过了硬性限制所设置的大小, 那么服务器立即关闭客户端。
- 软性限制( softlimit ): 如果输出缓冲区的大小超过了软性限制所设置的大小, 但还没超过硬性限制, 那么服务器将使用客户端状态结构的
obuf_soft_limit_ reached_time属性记录下客户端到达软性限制的起始时间; 之后服务器会继续监视客户端, 如果输出缓冲区的大小一直超出软性限制, 并且持续时间超过服务器设定的时长, 那么服务器将关闭客户端;如果不再超过的话就直接清零属性值,不关闭客户端
客户端的类型
普通客户端
- 直接按照之前的模式执行相关程序即可
Lua脚本的伪客户端
- Lua_client 伪客户端在服务器初始化的时候就创建了,服务器运行的整个生命期中会一直存在,服务器被关闭时, 这个客户端才会被关闭
服务器
命令请求的执行过程
发送请求
Redis 服务器的命令请求来自 Redis 客户端, 当用户在客户端中键人一个命令请求时,客户端会将这个命令请求转换成协议格式, 然后通过连接到服务器的套接字, 将协议格式的命令请求发送给服务器
graph LR
id1[用户]--键入命令请求-->id2[客户端]--将命令转换为协议的格式并发送-->id3[服务器]读取请求
客户端与服务器之间的连接套接字因为客户端的写入而变得可读,服务器将调用命令请求处理器:
- 读取套接字中协议格式的命令请求, 并保存到客户端的输入缓冲区里面
- 对输入缓冲区中的命令请求进行分析, 提取出命令请求中包含的命令参数, 以及命
令参数的个数, 然后分别将参数和参数个数保存到客户端的argv属性和argc 属性里面 - 调用命令执行器, 执行客户端指定的命令
命令执行
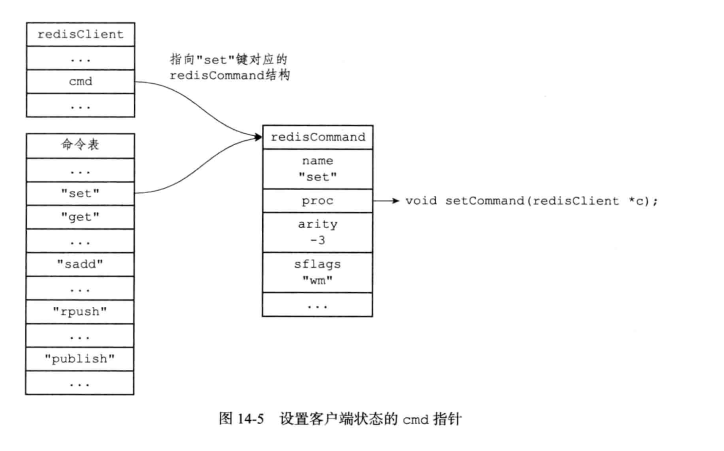
查找命令实现
根据客户端状态的 argv [ 0 ] 参数, 在命令表中查找参数所指定的命令, 并将找到的命令保存到客户端的 cmd 属性.
命令表(redisCommandTable)是一个字典,键是命令名字,值是redisCommand结构,记录了命令的实现信息
执行预备操作
检查上一步执行结果和执行命令的环境,权限等
调用命令实现函数
执行client->cmd->proc(client);,执行函数之后产生相应的命令回复,保存在客户端状态的输出缓冲区(buf和reply)
执行后续工作
记录日志等后续
将回复发送给客户端
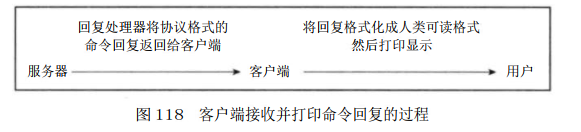
命令实现函数会将命令回复保存到客户端的输出缓冲区里面, 并为客户端的套接字关联命令回复处理器, 当客户端套接字变为可写状态时, 服务器就会执行命令回复处理器, 将保存在客户端输出缓冲区中的命令回复发送给客户端。 发送完之后将缓冲区清空.
客户端接受并打印命令回复
例子
SET KEY VALUE
先由客户端转换成协议
*3\r\n$3\r\nSET\r\n$3\r\nKEY\r\n$5\r\nVALUE\r\n并发送给服务器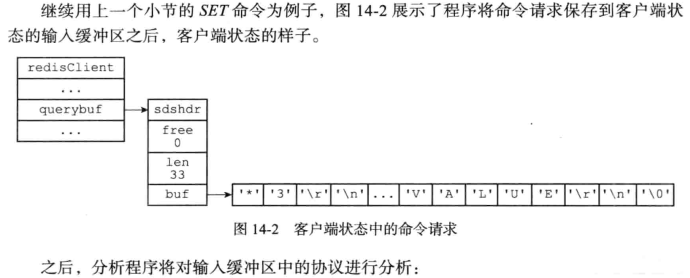

命令执行过程
查找命令实现
调用实现函数
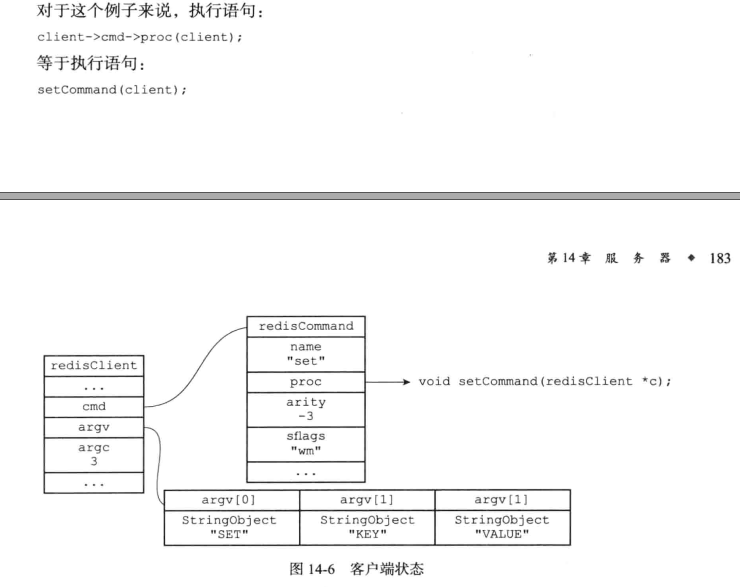
保存回复到缓冲区
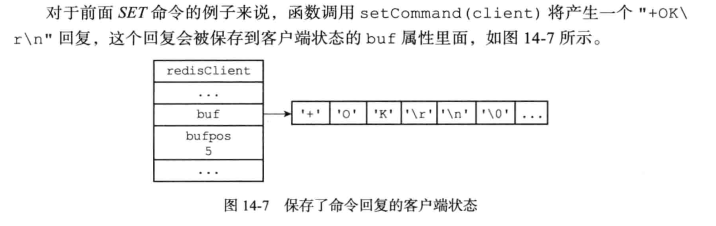
将
+OK\r\n发送给客户端客户端转换格式为
OK\n并显示
serverCron函数
默认每隔 100 毫秒执行一次
负责管理服务器的资源, 并保持服务器自身的良好运转
更新的内容:
更新服务器时间缓存
实时获取系统当前时间开销比较大,对于时间精度要求不是很高的使用地方使用缓存时间就可以.
//保存秒级精度的系统当前UNIX时间戳 redisAtomic time_t unixtime; //毫秒级精度的当前时间戳 mstime_t mstime; //微秒级精度的当前时间戳 ustime_t ustime;serverCron就是定时更新时间缓存的
更新LRU时钟
更新redis对象的空转时长属性
更新服务器每秒执行命令次数
嵌套调用的trackOperationsPerSecond函数抽样调查服务器一秒执行命令数量
//抽样记录服务器每秒执行的命令数量 struct { long long last_sample_time; /* Timestamp of last sample in ms */ long long last_sample_count;/* Count in last sample */ long long samples[STATS_METRIC_SAMPLES]; int idx; } inst_metric[STATS_METRIC_COUNT];每次执行和上次执行的记录结果做比较,估算这一秒的执行情况
更新服务器内存峰值记录
size_t stat_peak_memory;//已用内存峰值查看使用的内存数量,记录使用时的最大值
处理sigterm信号
为信号关联处理器sigtermHandler函数,负责在服务器接到sigterm信号的时候根据shutdown_asap决定是否关闭服务器(关闭之前先完成持久化操作)
管理客户端资源
clientsCron函数对客户端进行检查,连接是否超时,输入缓冲区是否过大.
管理数据库资源
databasesCron函数对数据库和其中的过期键,字典进行检查
执行被延迟的BGREWRITEAOGF
在服务器执行bgsave命令的期间, 如果客户端向服务器发来 BGREWRITEAOF 命令,那 么 服 务 器 会 将 命 令 的 执 行 时 间 延 迟 到 bgsave命 令 执 行 完 毕 之 后
初始化服务器
初始化状态结构
创建一个struct redisServer实例变量,设置默认值,创建命令表
主要由initServerConfig函数完成
载入配置选项
根据redis.config文件或者启动时指定的配置项配置其他选项
初始化服务器数据结构
创建服务器需要的除命令表之外的其他数据结构,需要用到之前的配置信息
initServre负责初始化这些数据结构和一些其他的设置操作,包括:
- 为服务器设置进程信号处理器。
- 创建共享对象: 这些对象包含 Redis 服务器经常用到的一些值, 比如包含”OK”和”ERR”回复的字符串对象, 包含整数 1 到 10000 的字符串对象等等, 服务器通过重用这些共享对象来避免反复创建相同的对象。
- 打开服务器的监听端口, 并为监听套接字关联连接应答事件处理器, 等待服务器正
式运行时接受客户端的连接。 - 为 serverCron 函数创建时间事件, 等待服务器正式运行时执行 serverCron 函数。
- 如果 AOF 持久化功能已经打开, 那么打开现有的 AOF 文件, 如果 AOF 文件不存在,
那么创建并打开一个新的 AOF 文件, 为 AOF 写入做好准备。 - 初始化服务器的后台 I/O 模块( bio ), 为将来的 I/O 操作做好准备
还原数据库状态
载入AOF或者RDB文件
执行事件循环
打开事件循环,之后就可以接受命令
多机数据库实现
复制
SLAVEOF可以让从服务器复制主服务器的内容,二者保存的数据是一致的
旧版复制功能
以前直接在重连的时候复制整个数据库的RDB文件,bgsave开销非常大(相当于重新执行了一次sync,期间对于主服务器不能执行其他命令,需要保存在缓冲区)
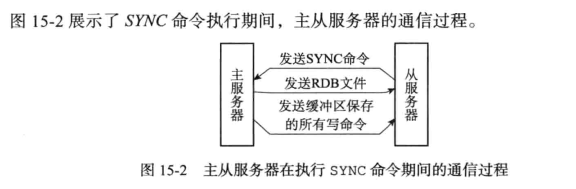
执行SYNC命令:
- 主服务器需要执行BGSAVE命令来生成 RDB 文件, 这个生成操作会耗费主服务器大量的 CPU、 内存和磁盘 I/O 资源。
- 主服务器需要将自己生成的 RDB 文件发送给从服务器, 这个发送操作会耗费主从服务器大量的网络资源( 带宽和流量 ), 并对主服务器响应命令请求的时间产生影响。
- 接收到 RDB 文件的从服务器需要载入主服务器发来的 RDB 文件, 并且在载入期间, 从服务器会因为阻塞而没办法处理命令请求。
每次主服务器改数据库之后都要传播该条命令
新版复制功能
使用PSYNC实现
- 完整重同步:初始复制主服务器,与之前的SYNC没有什么不同
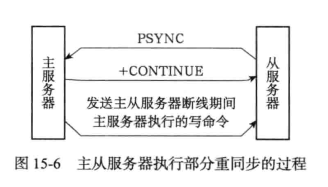
- 部分重同步:断线后重连复制,条件允许时直接将断开连接期间的写命令发给从服务器.
重连之后从服务器发送PSYNC命令,主服务器向从服务器返回+CONTINUE回复,表示执行部分重同步,从服务器接受回复,准备执行部分重同步,主服务器发送断线期间的写命令,从服务器接受并执行,完成同步
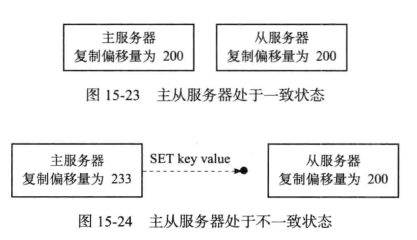
复制偏移量
主从服务器都会维护复制偏移量,主服务器发送n数据,从服务器接受n数据,都会分别给自己的复制偏移量添加n.
如果master和slave的偏移量是相同的,那么主从数据处于一致的状态
复制积压缓冲区
主服务器维护的一个FIFO队列,固定默认1MB大小
当master向slave传播命令时,会将命令写入到复制积压缓冲区,复制积压缓冲区记录了最近向slave传播的命令;并且为每个字节记录了相应的复制偏移量
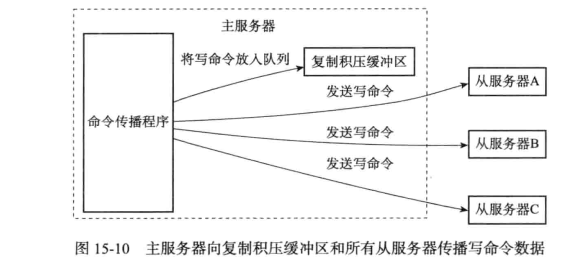
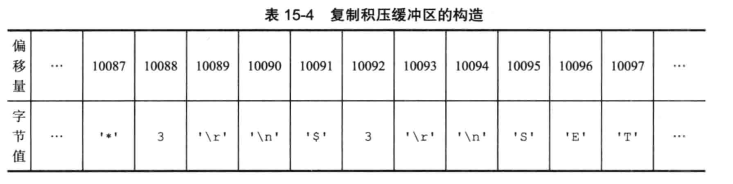
当slave断线后重新连接master时,向master发送PSYNC命令会将自己的复制偏移量发送给master。
master会根据这个偏移量决定对slave执行部分同步还是完全同步;
- slave的偏移量在复制积压缓冲区,执行部分同步 ;
- slave的偏移量不在复制积压缓冲区,则执行完全同步;
服务器运行ID
slave对master初次复制时,会保存master的运行id;
当slave重新连接到master时,slave向master发送之前保存的mater run id;
如果slave保存的master run id和重新连接的master run id不一致,(换了master),则执行完全同步;
相反,如果一致则尝试执行部分同步
PSYNC执行过程
PSYNC命令调用方式有两种:
PSYNC ? -1全量复制
当从服务没有复制过主服务器,或者从服务执行过SLAVEOF NO ONE命令(取消复制),那么从服务将发送PSYNC ?-1命令;PSYNC <runid> <offset>部分复制
从服务已经复制过主服务器,那么从服务将向主服务器发送PSYNC <runid> <offset>, runid是主服务器的id,offset服务器当前的偏移量;主服务器接受到
PSYNC <runid> <offset>命令后,主服务会判断是否能“部分同步”,向从服务回复相应的命令;
主服务向从服务的三种回复:
+FULLRESYNC <runid> <offset>执行完全重同步;+CONTINUE执行部分重同步;-ERR不支持psync同步操作,从服务将发送sync命令到主服务器,执行完全重同步;
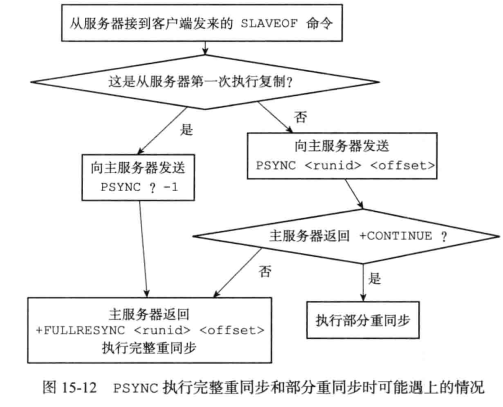
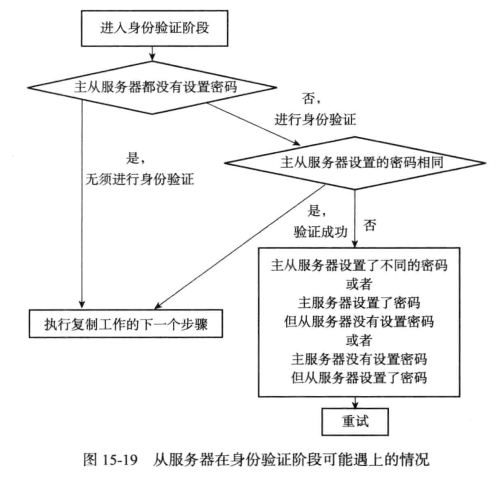
注意图片有个情况没写出来
设置主服务器的地址和端口
通过向从服务器发送SLAVE命令,可以让一个从服务器去复制一个主服务器
slaveof要做的主要是给“从服务”设置的“主服务”地址和端口,会保存到从服务器的masterhost和masterport属性中(replication.c/replicaofCommand)
slaveof是一个异步命令,完成设置后,会给客户端返回OK; 实际复制工作将在OK返回后真正开始执行;
执行
SLAVEOF 127.0.0.1 6379,设置好之后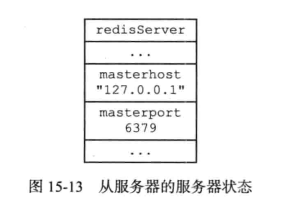
建立套接字连接
根据前一步保存的属性开始连接主服务器套接字(server.c/serverCron > replication.c/replicationCron > replication.c/connectWithMaster)
如果从服务和主服务器连接成功,从服务器会给这个套接字关联一个处理复制工作的文件处理器(replication.c/syncWithMaster),处理器完成后续工作,包括接受RDB文件,接受后续传来的写命令
主服务器在接受( accept ) 从服务器的套接字连接之后, 将为该套接字创建相应的客户端状态, 并将从服务器看作是一个连接到主服务器的客户端来对待, 这时从服务器将同时具有服务器和客户端两个身份.
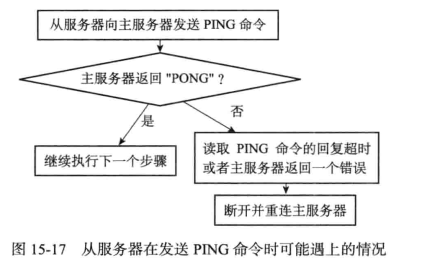
发送ping命令
- 检查套接字连接情况
- 检查主服务器是否能正常处理命令
身份验证
- 如果从服务器设置了 masterauth 选项, 那么进行身份验证。
- 如果从服务器没有设置 masterauth 选项, 那么不进行身份验证。
发送端口信息
从服务将执行
REPLCONF listen-port <port-number>,向主服务器发送从服务监听的端口号
主服务器接受到这个命令后,将从服务的端口号记录到客户端状态中的 slave_listening_port属性中

同步
从服务器向主服务器发送PSYNC命令
在同步操作执行之前, 只有从服务器是主服务器的客户端, 但是在执行同步操作之后, 他们互为客户端,因为主服务器也需要发送写命令给从服务器
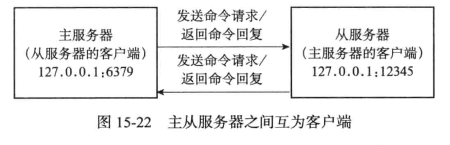
命令传播
写命令传播给从服务器
心跳检测
在命令传播阶段,从服务默认每秒一次的频率向主服务器发送 REPLCONF ACK <replicaiotn_offset> (replication_offset是当前从服务器的复制偏移量)
心跳检测的代码入口位于:server.c/serverCron > replication.c/replicationCron > replication.c/replicationSendAck
检测与主服务的网络连接状态
主从服务器通过发送和接受REPLCONF 命令检查网络连接是否正常;
如果从服务器超过一秒没有接收到从服务的REPLCONF 命令,主服务器就知道从服务连接出了问题;
主服务器对每个从服务器保存一个lag值记录上次收到心跳包的时间
辅助实现min-slave选项
redis的min-slave-to-write和min-salve-max-lag可以防止主服务在不安全的情况下执行写命令;
例如 主服务的min-slave-to-write和min-salve-max-lag配置如下:
min-salve-max-lag 10
min-slave-to-write 3
那么从服务的数量少于3个,或者3个从服务的延时(lag)值大于等于10秒时,主服务都不能执行写命令;
检测命令丢失
如果因为网络原因,主服务传播给从服务的命令丢失了。那么当从服务向主服务器放松RELPCONF ACK 命令时,主服务会发觉 从服务 的复制偏移量少于主服务的复制偏移量;
然后主服务会将丢失的部分发送给从服务器(这里是没有断线的部分重同步,与断线之后的PSYNC区分)